Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is the Average Age for Breast Cancer Diagnosis?
- Breast Cancer Risk by Age Group
- Factors That Influence Breast Cancer Risk
- Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
- Prevention and Early Detection
- Conclusion
Introduction
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting women worldwide. While many associate it with older age, it can occur at any stage of life. Understanding the relationship between breast cancer and age helps in identifying risks, taking preventive measures, and ensuring early detection. Early awareness and proactive screening can save lives, making it crucial for women of all ages to stay informed.
What is the Average Age for Breast Cancer Diagnosis?
The risk of developing breast cancer increases with age. According to global statistics:
- The average age of breast cancer diagnosis is around 62 years.
- However, younger women, especially in their 30s and 40s, are also at risk.
- Breast cancer in women under 30 is rare but not impossible.
- Postmenopausal women have a higher risk due to hormonal changes.
Interestingly, advances in medical research have shown that lifestyle, genetics, and environmental factors play a role in determining the age of onset. Regular check-ups and self-examinations are crucial for early detection, regardless of age.
Breast Cancer Risk by Age Group
Different age groups face varying levels of risk. Here’s a breakdown:
In Your 20s and 30s:
- Breast cancer is less common but can occur.
- Genetic factors (like BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations) play a major role.
- Dense breast tissue in younger women makes detection harder.
- Unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as poor diet and smoking, may contribute.
In Your 40s and 50s:
- The risk begins to increase significantly.
- Hormonal shifts, especially related to menopause, contribute.
- Lifestyle factors, such as diet, stress, and lack of exercise, impact risk levels.
- Mammograms are highly recommended by age 40.
After 60:
- More than 50% of breast cancer cases occur in women over 60.
- Slower cell repair and prolonged estrogen exposure elevate risk.
- Regular mammograms are crucial for early detection.
- Maintaining a healthy weight and staying active can help reduce risk.

Factors That Influence Breast Cancer Risk
Several factors contribute to breast cancer risk beyond just age. These include:
- Genetics: A family history of breast cancer increases risk.
- Hormonal Changes: Increased lifetime exposure to estrogen (early menstruation, late menopause, hormone replacement therapy).
- Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a poor diet can raise risk.
- Obesity: Higher body fat levels contribute to hormonal imbalances.
- Radiation Exposure: Prior radiation therapy to the chest can elevate risk.
- Environmental Factors: Long-term exposure to pollution, chemicals, and endocrine disruptors may also play a role.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Early detection can significantly improve survival rates. Watch for:
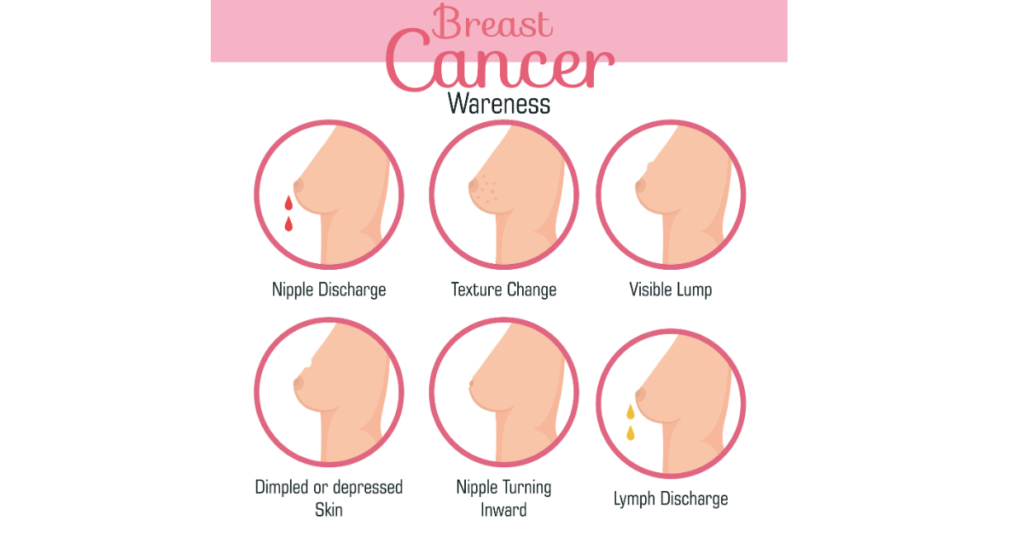
- Lumps or thickening in the breast or underarm.
- Changes in breast shape, size, or texture.
- Unexplained pain in the breast or nipple area.
- Nipple discharge (especially bloody or clear).
- Skin changes, such as dimpling, redness, or scaliness.
Even if you don’t have a family history, it’s important to stay vigilant and conduct regular self-examinations. Early diagnosis increases the chances of successful treatment.
Prevention and Early Detection
While breast cancer cannot always be prevented, reducing risk factors and prioritizing early detection can make a difference.
Preventive Measures:
- Regular Screening: Annual mammograms after age 40 (or earlier if high-risk).
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintain a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and avoid smoking.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: Reducing alcohol consumption lowers risk.
- Breastfeeding: It has been linked to a lower risk of breast cancer.
- Genetic Testing: If you have a family history, consult a doctor about BRCA gene testing.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity increases estrogen levels, which may contribute to cancer risk.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can impact hormonal balance, potentially influencing cancer risk.
The Importance of Mammograms
Mammograms help detect breast cancer before symptoms appear, improving treatment outcomes. Early-stage breast cancer has a 98% survival rate, reinforcing the importance of routine screening. Self-examinations and doctor visits should become a part of your routine.
Conclusion
Breast cancer can develop at any age, but being aware of risk factors, symptoms, and preventive measures can help in early detection and better management. If you’re in a high-risk group, talk to your doctor about personalized screening plans.
Your health is in your hands – stay informed, get screened, and prioritize your well-being. Every woman deserves the best chance at early detection and successful treatment.

